The term "youth violence" covers a broad spectrum of behaviors that can include fighting, bullying, and gang-related violence. Exposure to violence as a child can cause emotional and physical harm, including negative impacts on health and well-being that can follow a child into adulthood.
Youth violence and its diverse ramifications have long been a major challenge for American police officers, school staff, and municipal leaders. Preventing youth violence is a critical issue for many communities across the country.
Youth Violence Statistics
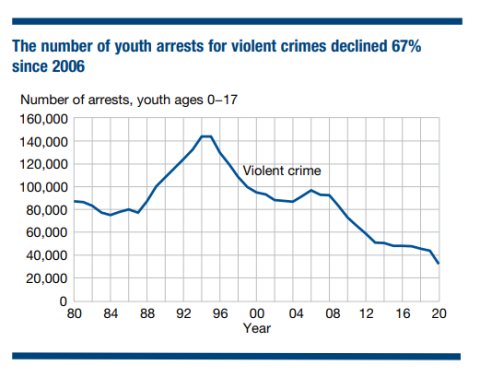
The estimated number of youth arrests for violent crimes, including murder, robbery, and aggravated assault, has declined since the mid-2000s, according to a fact sheet from the Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP) and the National Institute of Justice (NIJ).
According to the report, the number of violent crime arrests involving youth reached a new low in 2020 -- 78% below the 1994 peak, and half the number of arrests in 2010 (pictured).
Causes of Youth Violence
Adolescence is a common period for becoming involved in violence and gangs. In schools, gangs often engage in threats and intimidation, physical and cyberbullying, fighting, and other criminal activities that may involve drugs and weapons.
Another type of youth violence, teen dating violence, is an issue that can lead to serious short- and long-term effects. Examples of teen dating violence include physical and emotional harm and stalking. Once a teen experiences violence in one relationship, research has shown that they are at significant risk of experiencing violence in another.
Effects of Youth Violence
The impact of violence in schools extends beyond the individuals directly involved. It can also disrupt the education process and negatively affect youth and adults in the school and the surrounding community.
Research has shown that youth who experience or perpetrate violence at school are more likely to bully others -- both in school or in other situations outside of the classroom.
Youth who witness or experience violence in their community are also more likely to use drugs and alcohol and become involved in violence themselves.
Young victims of crime are generally underserved, and the systems responsible for caring for them can be fragmented and ineffective. The Office for Victims of Crime is committed to improving services for all victims of crime, including those exposed to different forms of violence.
How To Prevent Youth Violence
Research supported by OJJDP analyzed interventions to reduce youth gun and group violence. The study found that the most effective programs used case management and services, enhanced surveillance, outreach workers, and public perception campaigns.
Mentoring programs are another potentially beneficial component of youth gang violence intervention. For youth impacted by or involved with gangs, mentors can help them navigate challenges in life and achieve positive life outcomes.
In fiscal year 2021, OJJDP awarded nearly $23 million under the Youth Violence Intervention Initiative to address youth violence and provide services for children exposed to violence.
Since 2022, OJJDP has awarded nearly $47 million through the Enhancing School Safety To Address Youth Violence initiative to support schools and community-based organizations to address violence by youth.
Through the CrimeSolutions website, NIJ reviews programs and practices designed to prevent violence and provide services to those impacted by crime. The CrimeSolutions site includes information about a variety of topics, including crime in schools, youth gangs, and youth violence victimization.
April 24-28, 2023, is recognized as National Youth Violence Prevention Week. Founded in 2001, National Youth Violence Prevention Week allows communities to raise awareness and learn how to prevent youth violence to make schools and neighborhoods safer.
More on Youth Violence from OJP
Visit the following pages for additional information and resources produced or sponsored by the Office of Justice Programs and other federal agencies:
| Youth Violence Publications | Additional Youth Violence Resources |